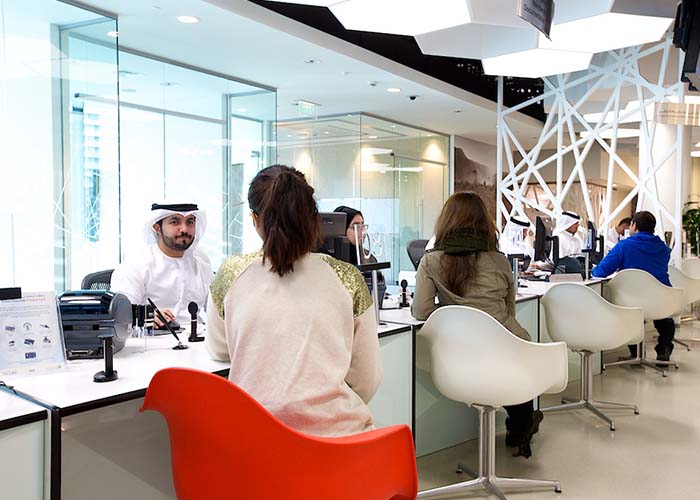
Plant assets are an integral part of a company’s long-term operations, and their management and accounting play a crucial role in the overall financial health and performance of a business. Assets such as equipment, machinery, buildings, vehicles, and more are assets commonly described as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Items labeled as PP&E are tangible, fixed, and not easy to liquidate.
PP&E is listed on a company’s balance sheet by adding its value minus accumulated depreciation. PP&E provides key functionality to help generate economic value to a company. For example, a company that needs to deliver its products gains value through the use of delivery vehicles, which would be considered PP&E.
- Although PP&E are noncurrent assets or long-term assets, not all noncurrent assets are property, plant, and equipment.
- Plant assets can vary widely depending on the nature of a company’s operations.
- A new press technology has just launched in the market, and the company owner decided to acquire the machine.
- The IFRS Foundation is a not-for-profit, public interest organisation established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable and globally accepted accounting and sustainability disclosure standards.
- When a company buys a new plant asset, it records the cost of the asset in its balance sheet.
- Proper management of the disposal of plant assets ensures transparency in financial reporting and helps maintain accurate records of a company’s asset inventory.
Here we will use all 4 methods to calculate the machine’s depreciation. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. https://accounting-services.net/ Below is a portion of Exxon Mobil Corporation’s (XOM) quarterly balance sheet from Sept. 30, 2018. The same process will be repeated every year at the end of the financial year. Mary Girsch-Bock is the expert on accounting software and payroll software for The Ascent.
What Are Noncurrent Assets?
Plant assets, also known as fixed assets, are tangible assets that are used in the production process or to generate revenue for a company over an extended period of time. These assets are not meant for resale and are expected to provide economic benefits for several years. Although PP&E are noncurrent assets or long-term assets, not all noncurrent assets are property, plant, and equipment. Intangible assets are nonphysical assets, such as patents and copyrights. They are considered to be noncurrent assets because they provide value to a company but cannot be readily converted to cash within a year. Long-term investments, such as bonds and notes, are also considered noncurrent assets because a company usually holds these assets on its balance sheet for more than one fiscal year.
Acquisition of Plant Assets
The PP&E account is often denoted as net of accumulated depreciation. This means that if a company does not purchase additional new equipment (therefore, its capital expenditures are zero), then Net PP&E should slowly decrease in value every year due to depreciation. The expected useful life of the machine is 7 years, and the salvage (scrap) value after 7 years will be $50,000.
For example, an auto manufacturer’s production facility would be labeled a noncurrent asset. Noncurrent assets may be subdivided into tangible and intangible assets—such as fixed and intangible assets. It is important for a company to maintain a certain level of inventory to run its business, but neither high nor low levels of inventory are desirable.
In certain asset-intensive industries, PP&E is the largest class of assets. In most cases, companies will list their net PP&E on their balance sheet when reporting financial results, so the calculation has already been done. Property, plant, plant meaning in accounting and equipment (PP&E) are long-term assets vital to business operations. Property, plant, and equipment are tangible assets, meaning they are physical in nature or can be touched; as a result, they are not easily converted into cash.
Understanding Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E)
As a result, it’s important to monitor a company’s investments in PP&E and any sale of its fixed assets. This would include long term assets such as buildings and equipment used by a company. Plant assets (other than land) will be depreciated over their useful lives. In the balance sheet of the business entity, these assets are recorded under the head of non-current assets as Plant, property, and equipment. A plant asset is an asset with a useful life of more than one year that is used in producing revenues in a business’s operations. Depreciation reduces the value of property, plant, and equipment on the balance sheet as the value of assets is lowered over time due to wear and tear and the reduction of their useful life.
Every year, the percentage is applied to the remaining value of the asset to find depreciation expense. In the initial years of the asset, the amount of depreciation expense is higher and decreases as time passes. The portion of ExxonMobil’s balance sheet pictured below from its 10-K 2021 annual filing displays where you will find current and noncurrent assets. Fixed assets include property, plant, and equipment because they are tangible, meaning that they are physical in nature; we may touch them.
The image below shows the opening, depreciation, and closing values for 7 years. Monte Garments is a factory that manufactures different types of readymade garments. The company also has a printing press for printing customized merchandise with brand designs. A new press technology has just launched in the market, and the company owner decided to acquire the machine. The cost of the machine is USD100,000, and it is expected to stay useful for five years with a residual value of USD10,000. The IFRS Foundation is a not-for-profit, public interest organisation established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable and globally accepted accounting and sustainability disclosure standards.
They are distinguished from current assets, such as cash and inventory, which are expected to be converted into cash within a year or the operating cycle of a business. Plant assets are a group of assets used in an industrial process, such as a foundry, factory, or workshop. These assets are a subset of the fixed assets classification, which includes such other asset types as vehicles, office equipment, and intangible assets. Plant assets fulfill the usual criteria for a fixed asset, which means that their initial cost exceeds the capitalization limit of the entity, and they are expected to be used for at least one year.
As the fixed assets last longer, the expenses are divided over the item until they’re useful. The value of PP&E is adjusted routinely as fixed assets generally see a decline in value due to use and depreciation. Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life and is used to account for declines in value. The total amount of a company’s cost allocated to depreciation expense over time is called accumulated depreciation. Plant assets and the related accumulated depreciation are reported on a company’s balance sheet in the noncurrent asset section entitled property, plant and equipment.
What is a plant asset?
PP&E items are commonly grouped into classes, which are groups of assets having a similar nature and use. Examples of PP&E classes are buildings, furniture and fixtures, land, machinery, and motor vehicles. Items grouped within a class are typically depreciated using a common depreciation calculation. Many items grouped into a PP&E class are assigned the same useful life for depreciation purposes. PP&E are assets that are expected to generate economic benefits and contribute to revenue for many years.
It provides transparency and accountability to stakeholders and assists in making informed decisions regarding investments, lending, and overall business operations. By accurately recording plant assets in accounting, businesses can track their investments and assess the value of their assets over time. Additionally, it allows for proper calculation of depreciation expense and provides transparency and accountability in financial reporting.
The only exception is land, which does not have a limited useful life, so cannot be depreciated. Other Standards have made minor consequential amendments to IAS 16. In June 2014 the Board amended the scope of IAS 16 to include bearer plants related to agricultural activity.